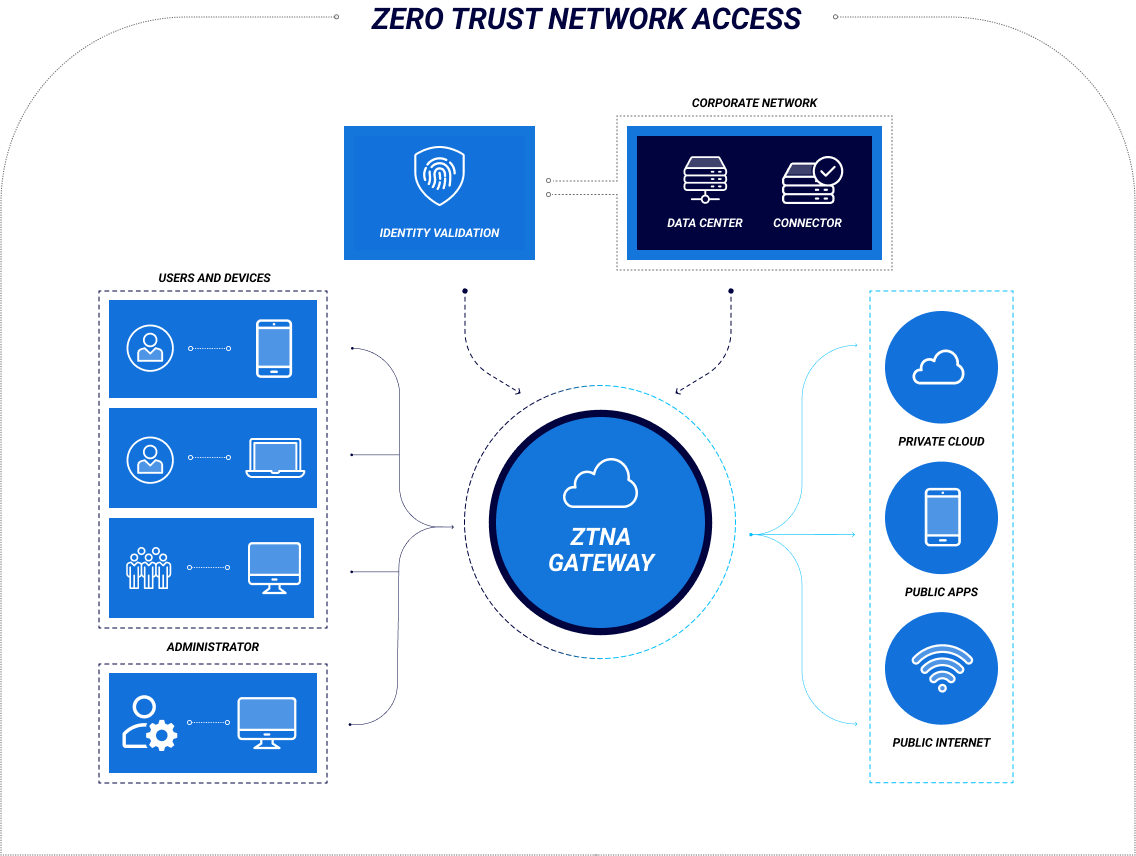
ZTNA is a software-defined security solution that shifts away from the traditional perimeter-centric approach to network security. It provides consistent, optimized protection with centralized control of access policies. It is essential as cloud migration, Direct Internet Access (DIA) and work-from-anywhere (WFA) trends dissolve legacy networks’ hard perimeters.
Invisible Infrastructure
Invisible infrastructure is a security concept that helps organizations isolate critical network assets from malicious users and devices. The key component is granular, application-centric access that reduces the attack surface and limits the lateral movement of attacks. Organizations must ensure only authorized third-party vendors or contractors can access their networks and applications. It can be complicated as companies converge networks or transition to multi-cloud environments. ZTNA solutions should be able to thwart unauthorized access and limit the damage resulting from a data breach. It should also be able to monitor user activity, including access requests and log-ins.
To implement ZTNA, a client or agent is installed on the device and sends information to a controller, such as a device’s location, security posture, date, and time. The controller then validates the information and grants connectivity through a gateway that shields applications from being accessed by unauthorized users or devices over the Internet.
Unlike software-defined perimeter (SDP), which only allows a single connection to each application, ZTNA uses micro-segmentation to segment and assign access to applications based on the workload level. This approach provides a more consistent security experience and enables more accessible abnormal behavior flagging for real-time analysis and investigation. It benefits organizations that need to keep their legacy systems and devices secure in a digital world.

Zero Trust Security
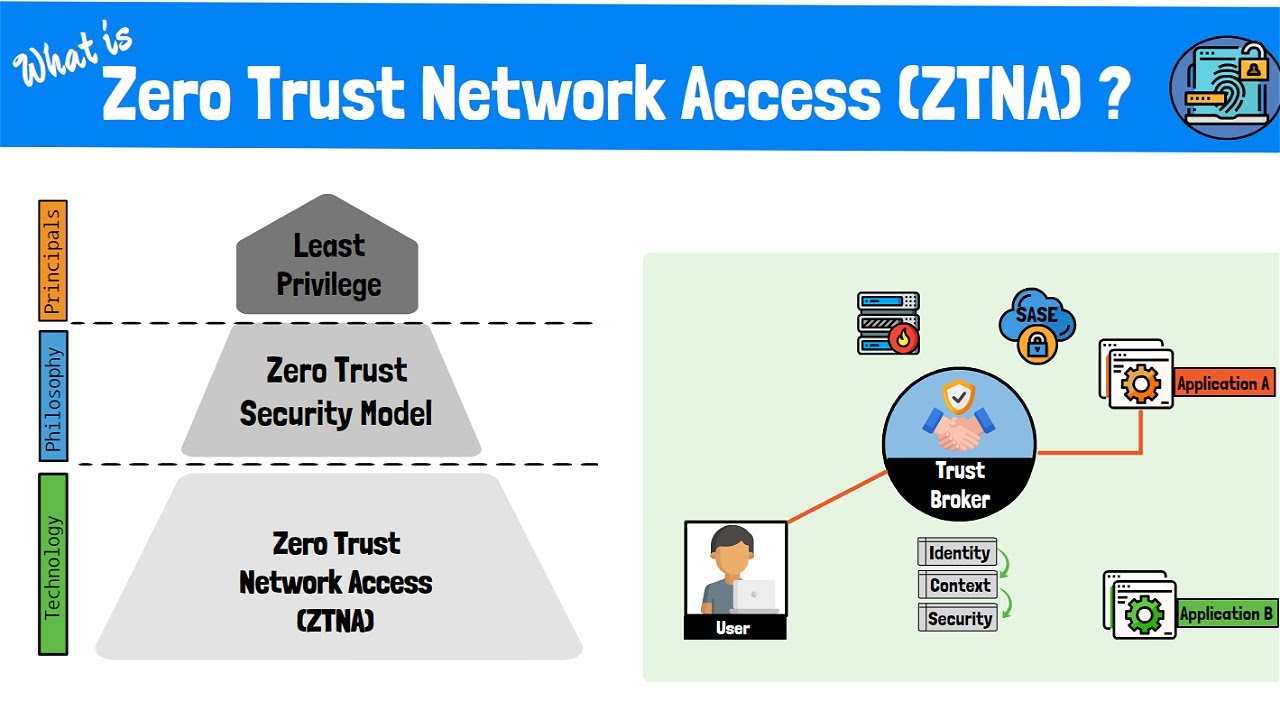
Zero trust security is a framework that enables organizations to secure data and network infrastructure against modern threats, including cybercriminals and ransomware. A departure from the traditional perimeter-focused defenses, zero trust is a layered approach that treats all network traffic as hostile, blocking it until an identity validates it.
The critical components of ZTNA include the following:
Monitor all connected devices and users, and keep them updated with patches. It prevents vulnerabilities from being exploited and keeps systems safe.
Apply the principle of least privilege to all users, from executives and IT teams to contractors and remote workers. It allows users to access the resources they need for business purposes, minimizing their exposure to sensitive network parts.
In addition to monitoring and validating, security teams should continuously assess user identities, applications, and data, leveraging telemetry from across the environment. Unlike scheduled evaluations, continuous assessments can detect suspicious activity and respond to threats more quickly.
Zero trust security is a team sport and requires the right people to make it happen. Team members can fill any knowledge gaps or gain specialized expertise through zero-trust training courses and certifications from recognized organizations.
Native App Segmentation
App user segmentation is a powerful marketing technique that divides users into smaller groups based on demographic information, in-app behaviors, and other factors. These segments are then used to target specific customers for ad campaigns. Using segmentation allows marketers to reach their business goals more efficiently, increase conversions, reduce churn, and improve customer retention.
Segmentation also helps app developers understand their customer’s needs and deliver highly relevant content that enhances their engagement with the app. It improves their user experience and increases revenue for the app.
This type of segmentation is based on behavior and includes things like spending and saving habits, credit card use, search history, and software features. It can also include demographic, geographic, psychographic, and socio-cultural factors.
Behavioral segmentation can help app developers determine what features or features not to offer to users. These can create a more personalized user experience, leading to higher engagement, increased revenue, and greater user loyalty.
Psychographic segmentation can be defined as a group of people with shared characteristics, such as personality traits, areas of interest, hobbies, values, and personal attitudes. Generally, this type of segmentation is used to identify customers who are likely to engage with your brand.
It is a critical element of ZTNA because it completely separates application access provisioning from network access. This isolation eliminates network vulnerabilities, such as infection by compromised devices, and restricts access to applications to authorized, authenticated users. Moreover, ZTNA establishes outbound-only connections so that the network and application infrastructure are never exposed to the Internet, making it impossible for unauthorized users to find your network.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption is a security solution restricting information from anyone but the recipient. It is a powerful way to protect your data and communications.
It is an important security feature for enterprises that require privacy. It also helps mitigate the threat of malware infection and ransomware attacks.
ZTNA separates application access provisioning from network access, eliminating vulnerabilities that can lead to infection by compromised devices and granting only authenticated, authorized users access to specific applications. Additionally, ZTNA makes outbound-only connections to hide the network and the applications it hosts from unauthorized users.

In addition, the IP addresses of resources on a ZTNA infrastructure are never advertised to the Internet, creating a “darknet” that renders the entire network untraceable.
Zero trust security is rapidly gaining traction within enterprises as they look to move away from traditional network-centric solutions. It is an essential component in a modern network security architecture that should be a part of the overall plan from the start. Organizations, including an endpoint-initiated approach and a service-initiated approach, can adopt several different models of ZTNA. Both options can be implemented on physical and virtual servers.